Translate this page into:
Undergraduate dental student’s perception regarding E-learning method versus Traditional classroom-based method: A questionnaire-based study

*Corresponding author: Vedika Bharat Jhunjhunwala, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Mahatma Gandhi Vidyamandir’s Karmaveer Bhausaheb Hiray Dental College and Hospital, Nashik, Maharashtra, India. vedikajhunjhunwala21@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Jhunjhunwala VB, Bhoosreddy SA. Undergraduate dental student’s perception regarding E-learning method versus Traditional classroom-based method: A questionnaire-based study. J Academy Dent Educ. 2023;9:46-53. doi: 10.25259/JADE_31_2023
Abstract
Objectives:
The objective of this questionnaire-based study is to investigate the perception of undergraduate dental students on E-learning and traditional classroom-based learning and how a blended mode of studies is beneficial for the students.
Material and Methods:
A survey of 20 questions regarding students’ perception toward e-learning and traditional classroom-based learning during COVID-19 was formulated using the Google Forms and circulated among undergraduate dental students all over the state of Maharashtra.
Results:
A total of 849 survey forms which were completely filled were considered in the analysis.
Conclusion:
535 (63.0%) students agreed that the e-learning method of education did not prepare them well for the practical part of the curriculum, whereas 617 (72.7%) students reported that activities included in e-learning should be blended with traditional classroom-based learning to make them more interesting and 531 (62.5%) students reported that blended mode of education would help to overcome drawbacks of traditional classroom-based learning. Furthermore, 526 (62.0%) students reported that the application of a blended mode of learning would help to overcome the problems faced by them during the e-learning mode of education alone.
Keywords
E-learning mode
Traditional classroom-based learning
Blended mode
COVID-19
Dental students
INTRODUCTION
The COVID-19 pandemic had a huge impact in all sectors of our lives.[1] The education system, including dental education, experienced significant disruption as most universities and educational institutes worldwide temporarily closed their doors.[2] Students accustomed to the traditional classroom setting had to transition to digital learning due to the pandemic. To ensure the continuation of academic activities, a range of electronic resources and strategies were employed. Some of the practices of academics used during the COVID-19 pandemic were virtual classrooms, flipped classrooms, web-based learning, computer-based learning, virtual classrooms, and digital content.[3-5] A real classroom has now been replaced by the virtual classroom.
Distance E-learning is defined as using computer technology to deliver training, including technology-supported learning.[6] A traditional classroom is defined as an educational place where the teacher delivers knowledge to the students in person without any third-party medium.
A blended mode of the study is defined as a style of education, in which students learn through electronic and online media as well as traditional face-to-face teaching.
Dental education is very different from the usual educational institutes because it involves interaction between the students and faculty, a major part of which involves learning of clinical and technical skills in the clinics and laboratories. It is critical in these times of the COVID-19 pandemic to assess how using e-learning tools for students was used as a sole way of teaching and instruction compares to place-, clinic, or laboratory-based learning.[7,8] Undoubtedly, dental education is a crucial profession that demands extensive preparation from educators. This preparation encompasses not only expertise in various specialties within the discipline but also a deep understanding of effective teaching and learning methodologies.[9] In addition, how the trend of E-learning influences perception, confidence, and satisfaction among students is pivotal for the development of future health professionals.[4,10] While there is limited evidence indicating that e-learning courses can be comparable to classroom instructions and lead to high levels of student satisfaction, there is a lack of comprehensive data on the perception and satisfaction of E-learning among health sciences students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Hence, we conducted a questionnaire-based study to assess the perception of undergraduate dental students on E-learning and traditional classroom-based learning. Furthermore, we seek to explore the benefits of a blended learning approach for students.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
This cross-sectional questionnaire-based study was conducted among undergraduate dental students of the state of Maharashtra. The study population included undergraduate dental students from the 1st year to final year. The survey was conducted using a questionnaire comprising 20 questions written in English and validated through a pilot study. The study was conducted over a period of 3 months, i.e., March 1, 2022 to –May 31, 2022. Convenience sampling method was done to collect responses. It was voluntary participation, and informed consent was obtained from those who participated in the study. All the students were supplied with an information sheet regarding the nature and purpose of the study. Permission to conduct the survey was obtained from the KBH Dental College Institutional Ethics Committee (MGV/KBHDC/937/2021-22). A questionnaire of 20 questions was developed using Google Forms. This questionnaire was circulated among undergraduate students of the dental faculty using the online web. This was done mainly through Whatsapp groups, Whatsapp statuses, and E-mails. Total 849 responses were recorded. Only the forms with all the responses recorded were included.
The questionnaire comprised 20 questions. Information such as the year the student was studying in, type of device used for E-learning, any challenges faced, and advantages and disadvantages of both traditional and virtual learning methods were recorded. Moreover, information such as measures to improve the experience of E-learning, their perception toward a blended method of learning, and any suggestions to improve the teaching methods in the future was recorded.
Inclusion criteria
Undergraduate dental students studying in private dental colleges
Undergraduate students studying in government dental colleges.
Exclusion criteria
Incompletely filled survey forms
Dental students outside the state of Maharashtra 3. Postgraduate dental students.
Statistical analysis
The obtained data were analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software for windows version 20.0. After all the responses were recorded, appropriate statistical analysis was carried out using the statistical software SPSS. Chi-square test was used for the analysis. A P = 0.05 was used as a cut-off level for statistical significance.
RESULTS
In the study, we found that a maximum of 333 (39.2%) students from 4th year participated in the study followed by 230 (27.1%) students from 1st year, 229 (27.0%) students from 3rd year, and 57 (6.7%) students from 2nd year [Figure 1]. We further assessed the E-learning mode of education, out of 849 students, majority students 787 (92.7%) used smartphones, whereas only 118 (13.9%) students used laptop followed by 34 (4.0%) who used Tablet and 12 (1.4%) of them used personal computers for E-learning mode of education [Figure 2]. Various challenges faced by the students were assessed. It was found that maximum of 590 (69.5%) students faced challenges due to poor internet connection during the E-learning mode of education, followed by 289 (34.0%) students who faced challenges due to fatigue, 226 (26.6%) students that faced challenges due to a lack of time management, and 49 (5.8%) students that faced challenges because of computer literacy [Figure 3]. Interestingly, there are many perks of the online method of learning, out of which it was observed that 519 (61.1%) students responded that “no traveling required” is the main perk of E-learning, whereas 494 (58.2%) students responded that the “availability of pre-recorded lectures.” 348 (41.0%) students responded that “time feasibility” and 83 (9.8%) students responded that “better interaction with the faculty” are the perks of the online method of learning [Figure 4]. There are many perks of traditional classroom-based methods of learning, out of which it was observed that 559 (65.8%) students responded to “good discipline and attention during lectures” as the main perk of traditional classroom-based learning; also 551 (64.9%) students responded to “better understanding of the subject,” 510 (60.1%) students responded to “better interaction with the faculty during the lecture,” and 333 (39.2%) students responded to “helps in personality development as the perks of traditional classroom-based methods of learning” [Figure 5]. From the above figure, it was observed that a maximum of 512 (60.3%) students reported that “lack of practical knowledge” is the main disadvantage of the E-learning mode of education, followed by 445 (52.4%) students who reported that E-learning causes increased screen time and decreased attention, respectively. Furthermore, 356 (41.9%) and 314 (37.0%) students reported that decreased interaction and decreased discipline were disadvantages of the E-learning mode, respectively [Figure 6]. From Table 1, it was seen that 393 (46.3%) students reported that there are no disadvantages to traditional classroom-based learning, whereas 281 (33.1%) and 259 (30.5%) students reported that travel expenses and learning are confined to fixed timings are the disadvantages of traditional classroom-based learning, respectively [Figure 7]. It was observed that 538 (63.4%) students mentioned that sharing relatable videos and practical images, and 483 (56.9%) said that adding PowerPoint presentations, both helped the students to learn better in the E-learning mode of education, whereas 271 (31.9%) students were reported that online quiz sessions also helped in making E-learning mode of education interesting [Figure 8]. It was observed that 475 (55.9%) students agreed that lectures become monotonous after a point of time, 367 (43.2%) said that lack of visual aids, 181 (21.3%) said that lack of interaction, all were the drawbacks of traditional classroom that can be overcome by the application of blended mode of learning [Figure 9].
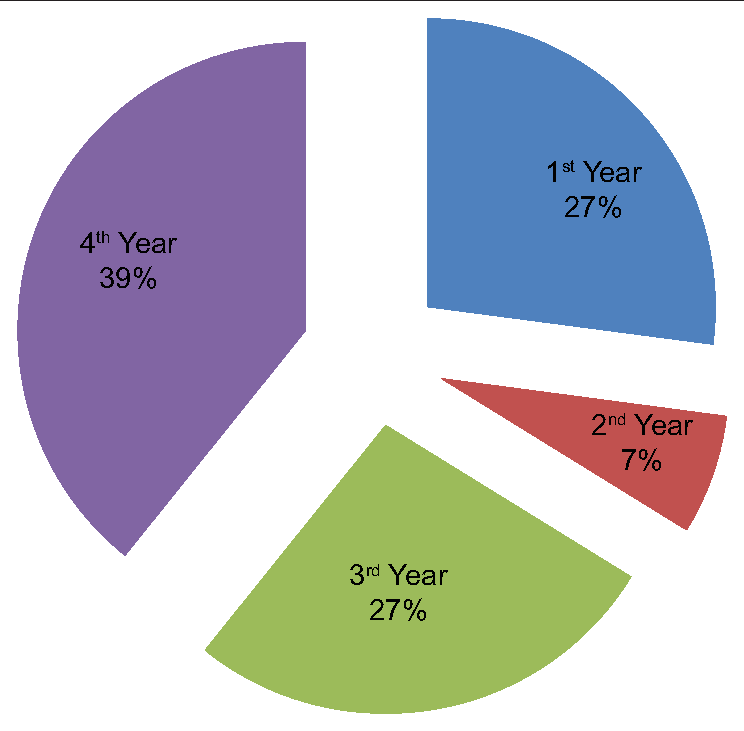
- Graph showing the distribution of participants according to year of studying.
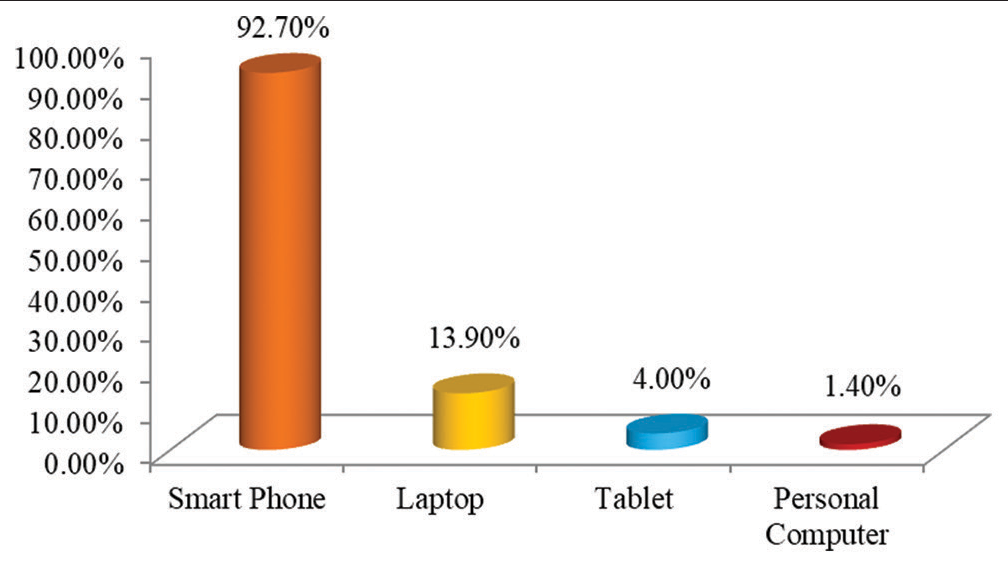
- Graph showing the distribution of participants according to device used for E-learning mode of education.
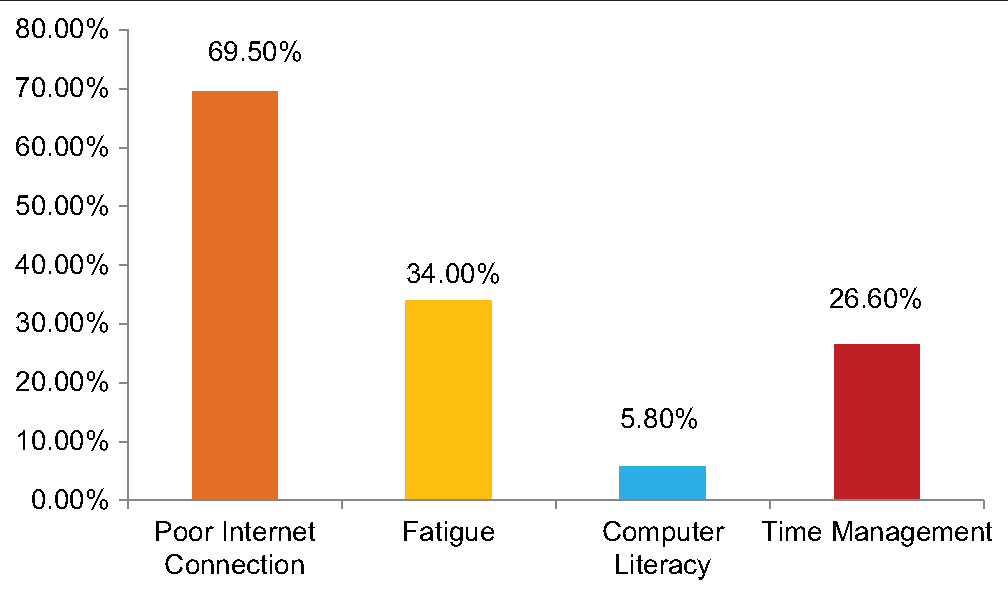
- Graph showing the distribution of participants according to challenges faced during E-learning mode of education.
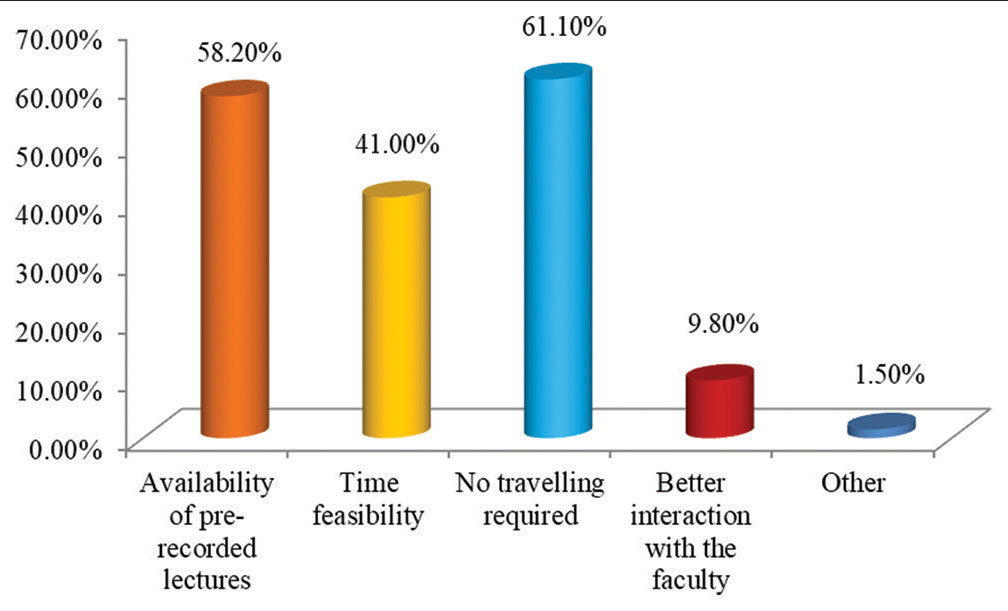
- Graph showing perks of online method of learning.
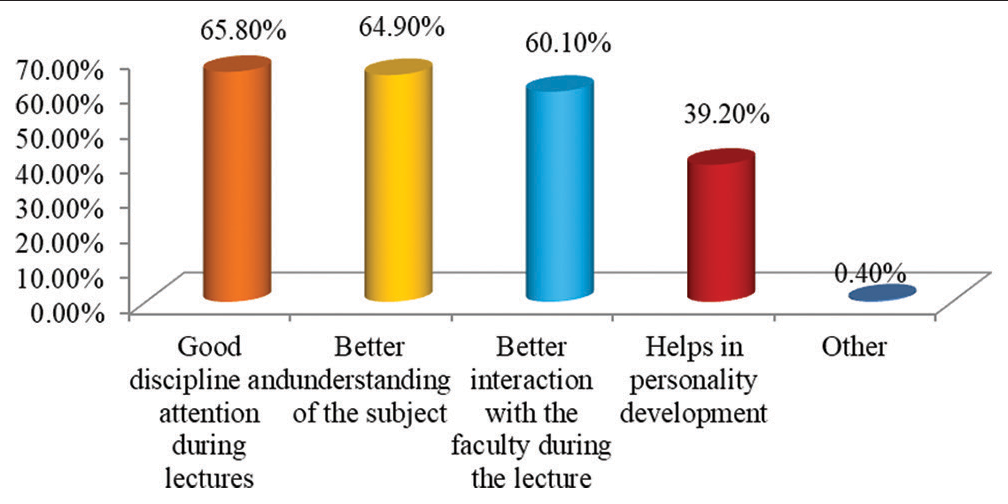
- Graph showing perks of traditional classroom-based methods of learning.
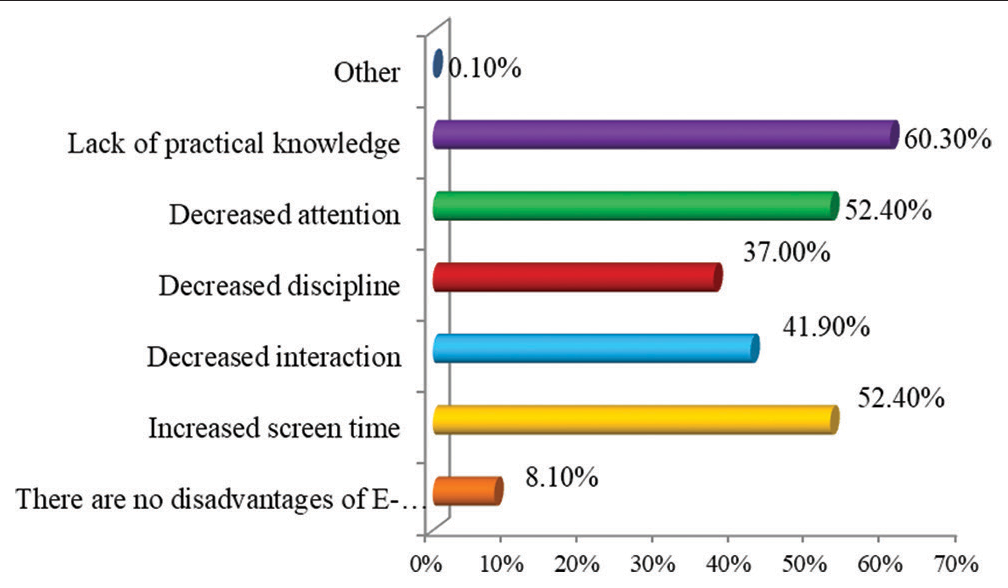
- Graph showing disadvantages of E-learning mode.
| Items | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Year of studying | ||
| 1st year | 230 | 27.1 |
| 2nd year | 57 | 6.7 |
| 3rd year | 229 | 27.0 |
| 4th year | 333 | 39.2 |
| Device use for E-learning mode of education | ||
| Smart phone | 787 | 92.7 |
| Laptop | 118 | 13.9 |
| Tablet | 34 | 4.0 |
| Personal computer | 12 | 1.4 |
| Challenges faced during E-learning mode of education | ||
| Poor internet connection | 590 | 69.5 |
| Fatigue | 289 | 34.0 |
| Computer literacy | 49 | 5.8 |
| Time management | 226 | 26.6 |
| Perks of online method of learning | ||
| Availability of pre-recorded lectures | 494 | 58.2 |
| Time feasibility | 348 | 41.0 |
| No traveling required | 519 | 61.1 |
| Better interaction with the faculty | 83 | 9.8 |
| Other | 13 | 1.5 |
| Perks of traditional classroom based methods of learning | ||
| Good discipline and attention during lectures | 559 | 65.8 |
| Better understanding of the subject | 551 | 64.9 |
| Better interaction with the faculty during the lecture | 510 | 60.1 |
| Helps in personality development | 333 | 39.2 |
| Other | 3 | 0.4 |
| Disadvantages of E-learning mode | ||
| There are no disadvantages of E-learning method | 69 | 8.1 |
| Increased screen time | 445 | 52.4 |
| Decreased interaction | 356 | 41.9 |
| Decreased discipline | 314 | 37.0 |
| Decreased attention | 445 | 52.4 |
| Lack of practical knowledge | 512 | 60.3 |
| Other | 1 | 0.1 |
| Disadvantages of traditional classroom based learning | ||
| There are no disadvantages of traditional classroom-based learning | 393 | 46.3 |
| Travel expenses | 259 | 30.5 |
| Learning is confined to fixed timings | 281 | 33.1 |
| Strain to the eyes | 71 | 8.4 |
| Other | 12 | 1.4 |
| Activities helped to learn better in E-learning mode of education | ||
| PowerPoint presentations | 483 | 56.9 |
| Sharing relatablevideos and images practical | 538 | 63.4 |
| Online quiz sessions | 271 | 31.9 |
| Seminars presented by students in groups | 191 | 22.5 |
| Other | 1 | 0.1 |
| Drawbacks of traditional classroom can be overcome by the application of blended mode of learning | ||
| Decreased attention and discipline | 197 | 23.2 |
| Lectures become monotonous after a point of time | 475 | 55.9 |
| Lack of visual aids | 367 | 43.2 |
| Lack of interaction | 181 | 21.3 |
| Other | 3 | 0.4 |
| Drawbacks of E-learning method can be overcome by application of blended mode of education | ||
| Decreased interaction | 364 | 42.9 |
| Decreased attention | 387 | 45.6 |
| Lack of practical knowledge | 571 | 67.3 |
| Other | 1 | 0.1 |
| Advantages of blended mode of learning | ||
| There are no advantages of blended mode of learning | 100 | 11.8 |
| It enables us to become more involved in the learning process | 438 | 51.6 |
| Information can be obtained in more than one way | 414 | 48.8 |
| Clinical images of lesions/conditions in the form of PowerPoints during lectures help in better visualization | 483 | 56.9 |
| Availability of instructional videos for dental procedures help in better understanding | 414 | 48.8 |
| Mode of education like to continue | ||
| E-learning | 59 | 6.9 |
| Traditional classroom-based learning | 296 | 34.9 |
| Blended mode of studying | 494 | 58.2 |
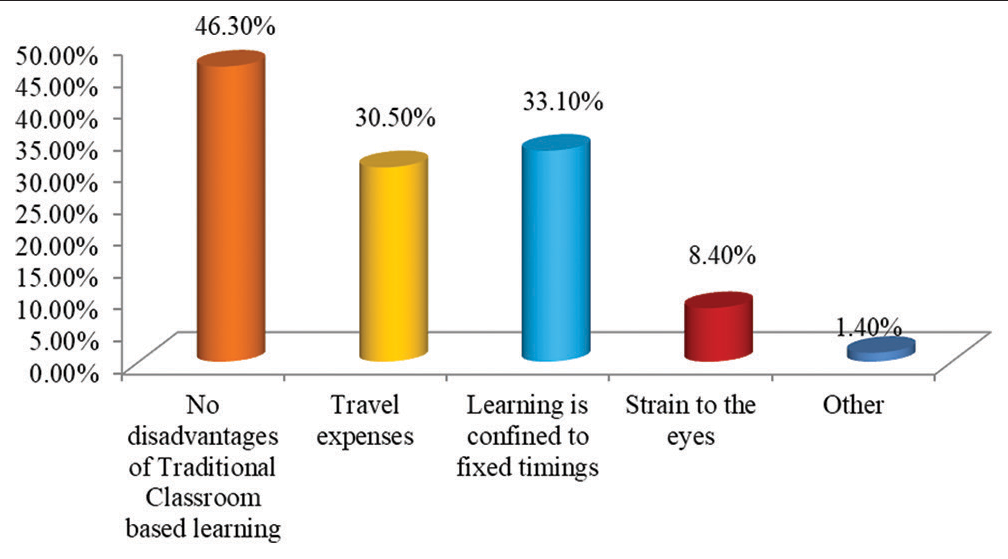
- Graph showing disadvantages of traditional classroom-based learning.
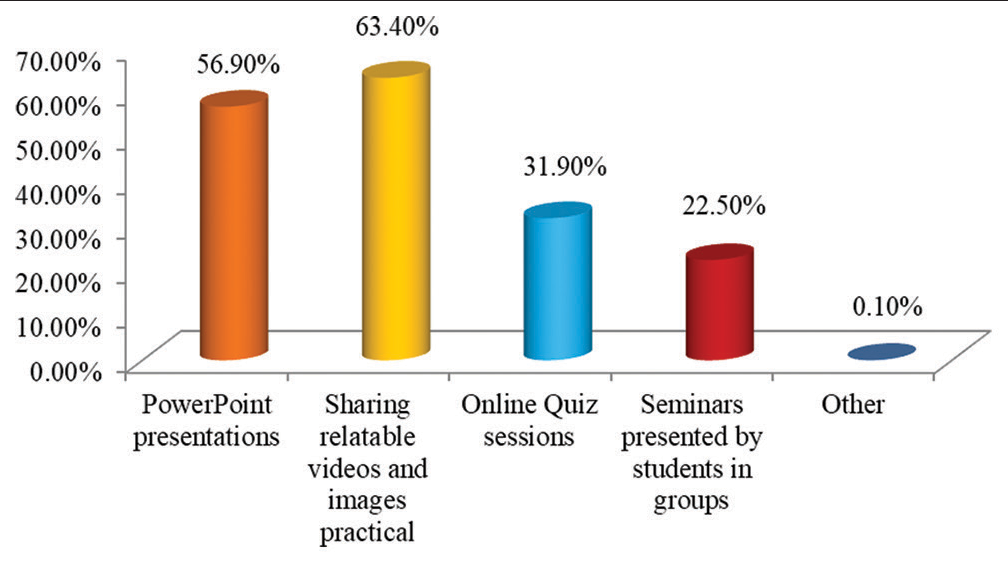
- Graph showing activities helped you learn better in the E-learning mode of education.
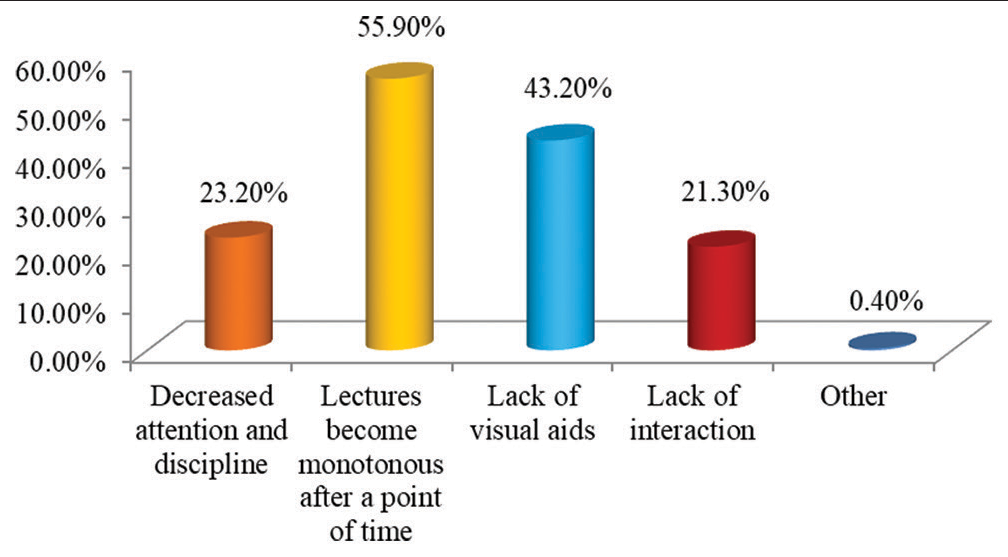
- Graph showing drawbacks of traditional classroom can be overcome by the application of blended mode of learning.
It was observed that 571 (67.3%) students said that a lack of practical knowledge, 387 (45.6%) agreed that decreased attention, and 364 (42.9%) said that decreased interaction are the drawbacks of E-learning can be overcome by the application of blended mode of learning [Figure 10].
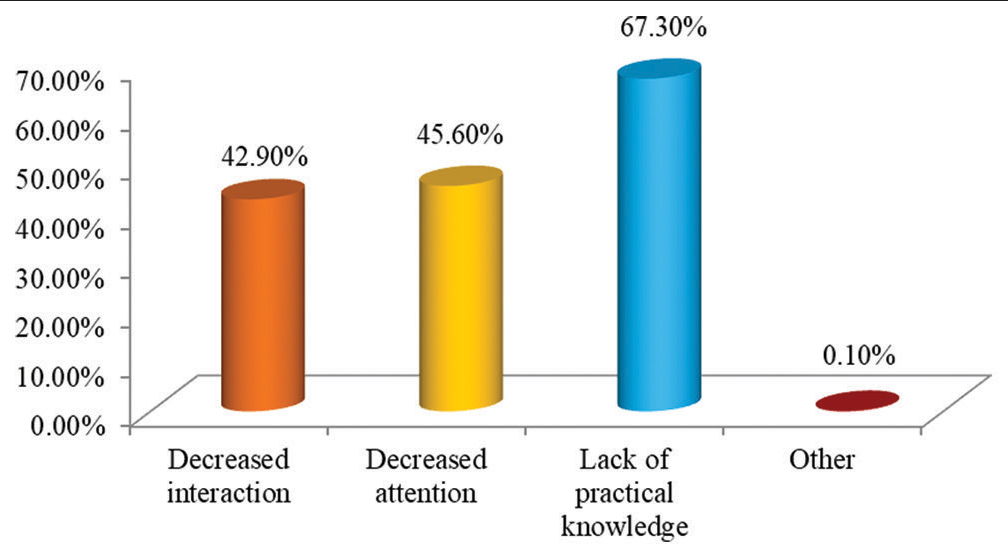
- Graph showing drawbacks of E-learning method can be overcome by application of blended mode of education.
It was observed that 483 (56.9%) students reported that clinical images of lesions/conditions in the form of PowerPoints during lectures help in better visualization, and 438 (51.6%) students reported that the blended mode of learning enables them to become more involved in the learning process, 414 (48.8%) said that information can be obtained in more than one way and the availability of instructional videos for dental procedures that help in better understanding [Figure 11].
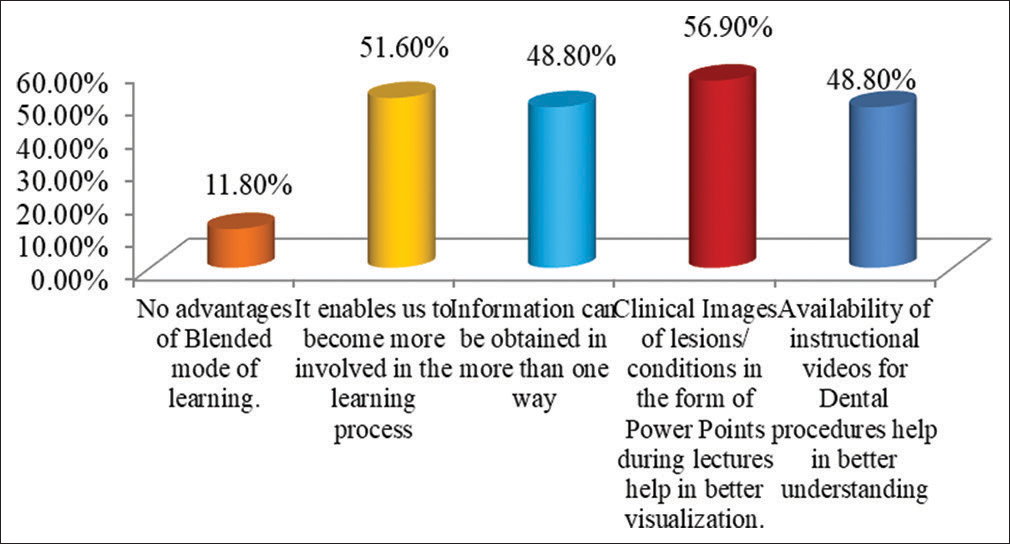
- Graph showing advantages of blended mode of learning.
It was found that 686 (80.8%) students reported that traditional classroom-based learning is better for conducting lectures for the theoretical part of academics only. 807 (95.1%) students reported that traditional classroom-based learning is better for the practical part of academics and 764 (90.0%) students reported that traditional classroom-based learning helps to interact more during lectures when compared to the E-learning mode of education. 767 (90.3%) students reported that, during traditional classroom-based learning, there was more discipline and that they could be more attentive compared to the E-learning mode of education [Figure 12]. It can be concluded that 535 (63.0%) students agreed that the E-learning method of education did not prepare them well for the practical part of the curriculum, whereas 617 (72.7%) students reported that activities included in E-learning should be blended with traditional classroom-based learning to make them more interesting and 531 (62.5%) students reported that blended mode of education would help to overcome drawbacks of traditional classroom-based learning. Furthermore, 526 (62.0%) students reported that the application of a blended mode of learning would help to overcome problems faced by them during the E-learning mode of education alone [Figure 13].
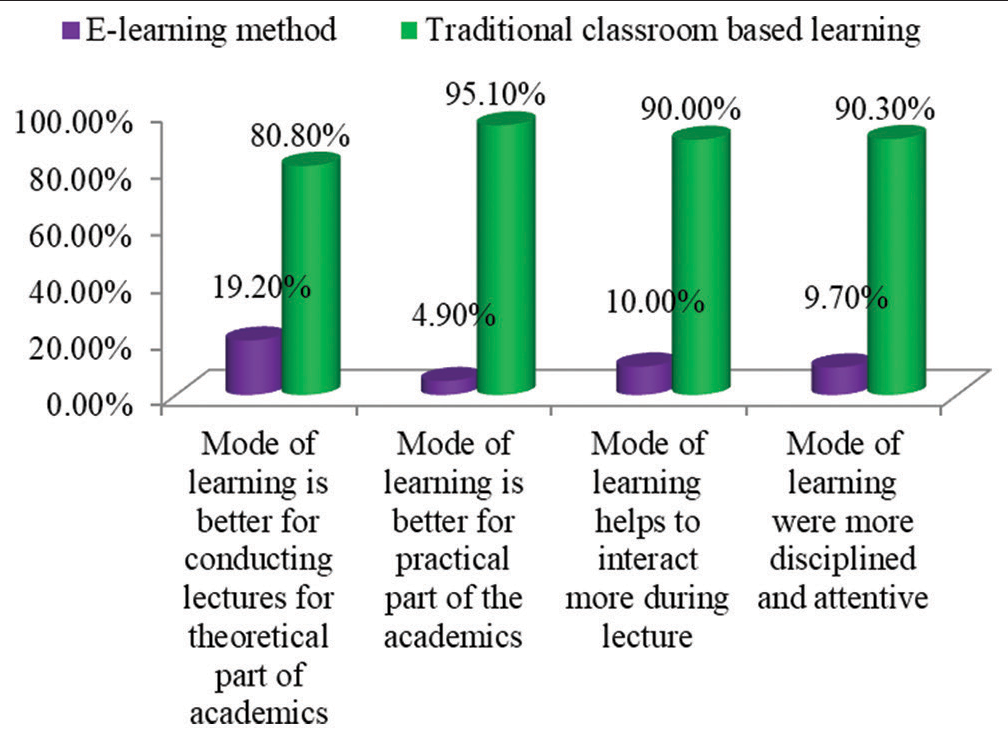
- Graph showing comparisons of E-learning method and traditional classroom based learning.
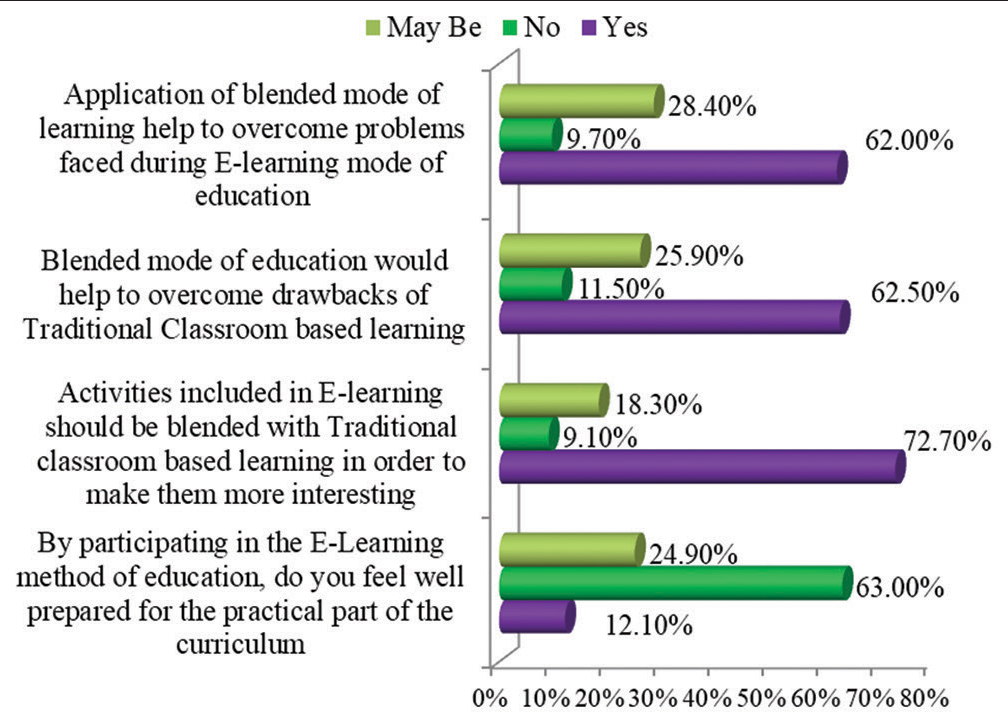
- Graph showing comparisons of learning mode of education.
Finally, it was seen that 494 (58.2%) students chose the blended mode of education over traditional classroom and e-learning mode of education, whereas 296 (34.9%) students wanted to continue with traditional classroom-based learning, and only about 59 (6.9%) students found E-learning as the best mode of learning [Figure 14].
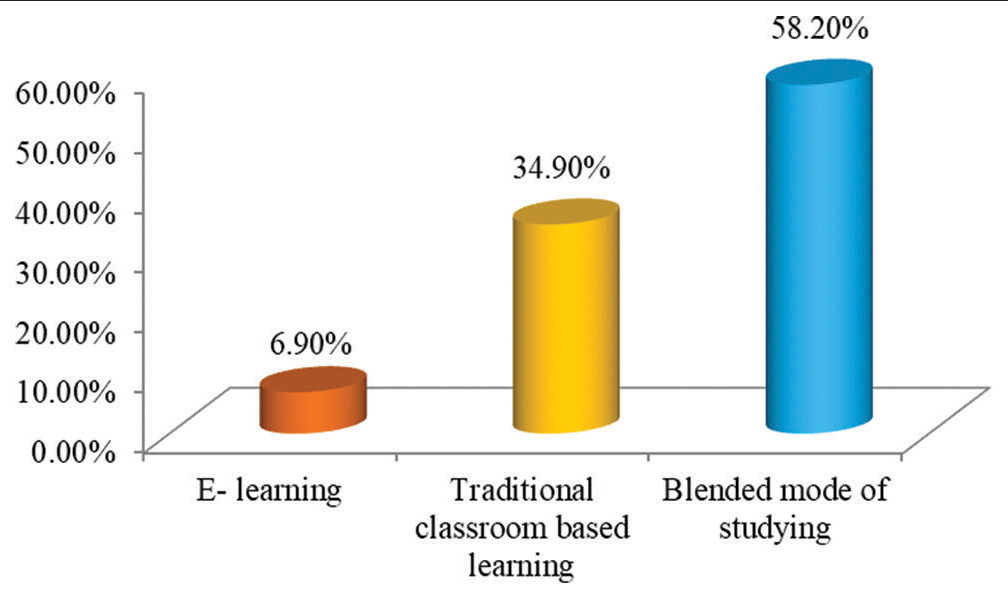
- Graph showing the mode of education to continue.
DISCUSSION
We conducted a questionnaire-based study to evaluate the perception of dental students toward the E-learning method during the COVID-19 pandemic. Out of total 849 participants, majority students were in the final year followed by 3rd year and 2nd year. Smartphones were the preferred mode of devices used as the E-learning platform. In other studies also, students preferred using smartphone as the preferred device to attend the online classes.[11,12] The reason for this can be easy availability and user-friendly interface of smartphones. Many studies also mentioned a lack of motivation due to various reasons among the students.[13] Students encounter various challenges in E-learning, including unreliable Internet connections, insufficient learning materials, interruptions in electricity supply, ambiguous course content, overwhelming assignment loads, limited interaction with teachers, conflicts with domestic responsibilities, unfavorable learning environments, physical health problems such as weak eyesight, and mental health difficulties.[14] We found that many students were not motivated due to difficulties such as disruptions in the Internet connections, fatigue, managing the time, and some were not technology savvy. E-learning offers several benefits, such as enhanced convenience, unrestricted access to resources regardless of time and location, and cost and environmental advantages by reducing expenses and air pollution.[15] In addition, online learning has demonstrated greater effectiveness in knowledge retention compared to traditional classroom-based education. In our study also, many students responded that the availability of pre-recorded lectures, feasibility of time, saving the time to travel, etc., were few advantages experienced. However, the traditional learning methods have benefits such as better student–teacher communication, better discipline, and communication are maintained.
In dental professional schools, the simulation laboratory courses and clinical exposure to patients are of central importance. The students were not able to get hands-on experience, and this was the main drawback in dental education.[16-18] Students in our study also reported the same findings. The use of audiovisual aids in the E-learning method improved the experience of students. Moreover, adding activities such as quiz also engaged student’s attention.[19]
With the pandemic weaning off, blended learning became a popular teaching method. The clinical lesions in a visual form helped students gain a better perspective. Overall, the students agreed that the conventional method of teaching was better than E-learning. For the best of student’s interests, the E-learning method should be blended with the traditional classroom methods.
CONCLUSION
Each method of education, i.e., traditional classroom based or E-learning has their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Dentistry is a skill-based program. Hence, students in our study found that the E-learning method did not prepare them well for practical aspects of the curriculum and that traditional classroom-based learning is important for the same. Nevertheless, the traditional model of education had problems of monotonicity after a point of time, lack of visual representations, etc.
The students shared how combining both the methods can help us overcome these drawbacks. Students shared that having access to pre-recorded videos of lectures will help them to watch and learn whenever it is feasible. Organizing quiz sessions, providing PowerPoint presentations, and visual representation (clinical photos) during traditional classroom-based methods would help the lectures to be interesting and that the students will be more involved. Maximum number of students would like to continue with a blended mode of studies which is incorporation of traditional classroom-based learning and E-learning.
Acknowledgment
We acknowledge all the undergraduate dental students from all over the state of Maharashtra who participated in this questionnaire-based survey by filling out the Google Forms circulated among them.
Ethical approval
The research/study is approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee at KBH Dental College, number MGV/KBHDC/937/2021-22.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as there are no patients in this study.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Distance learning in clinical medical education amid COVID-19 pandemic in Jordan: Current situation, challenges, and perspectives. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20:341.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Sustaining academics during COVID-19 pandemic: The role of online teaching-learning. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:1220-21.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perceptions of medical students towards online teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic: A national cross-sectional survey of 2721 UK medical students. BMJ Open. 2020;10:e042378.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E-Learning perception and satisfaction among health sciences students amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Work. 2020;67:549-56.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Student perspective of classroom and distance learning during COVID-19 pandemic in the undergraduate dental study program universitas Indonesia. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20:392.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on medical education: Medical students' knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding electronic learning. PLoS One. 2020;15:e0242905.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distance learning in the era of COVID-19. Arch Dermatol Res. 2021;313:389-90.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Online learning in the time of COVID-19. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020;34:101669.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Students' and lecturers' perspective on the implementation of online learning in dental education due to SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): A cross-sectional study. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20:354.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtual learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: A disruptive technology in graduate medical education. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:2635-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perception of dental students towards the online method of dental education during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2022;12:223-7.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Student use of mobile devices in university lectures. Aust J Educ Technol. 2014;30:415-26.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Motivating online learning: The challenges of COVID-19 and Beyond. Asia Pac Educ Res. 2021;30:187-90.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Difficulties in remote learning: Voices of Philippine university students in the wake of COVID-19 crisis. Asian J Distance Educ. 2020;15:147-58.
- [Google Scholar]
- Students' perception of online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:e24821.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497-506.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Incubation period of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections among travelers from Wuhan, China, 20-28 January 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020;25:2000062.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathogenicity and transmissibility of 2019-nCoV-A quick overview and comparison with other emerging viruses. Microbes Infect. 2020;22:69-71.
- [Google Scholar]
- Picture of a pandemic: Visual aids in the COVID-19 crisis. J Public Health. 2020;42:483-5.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






